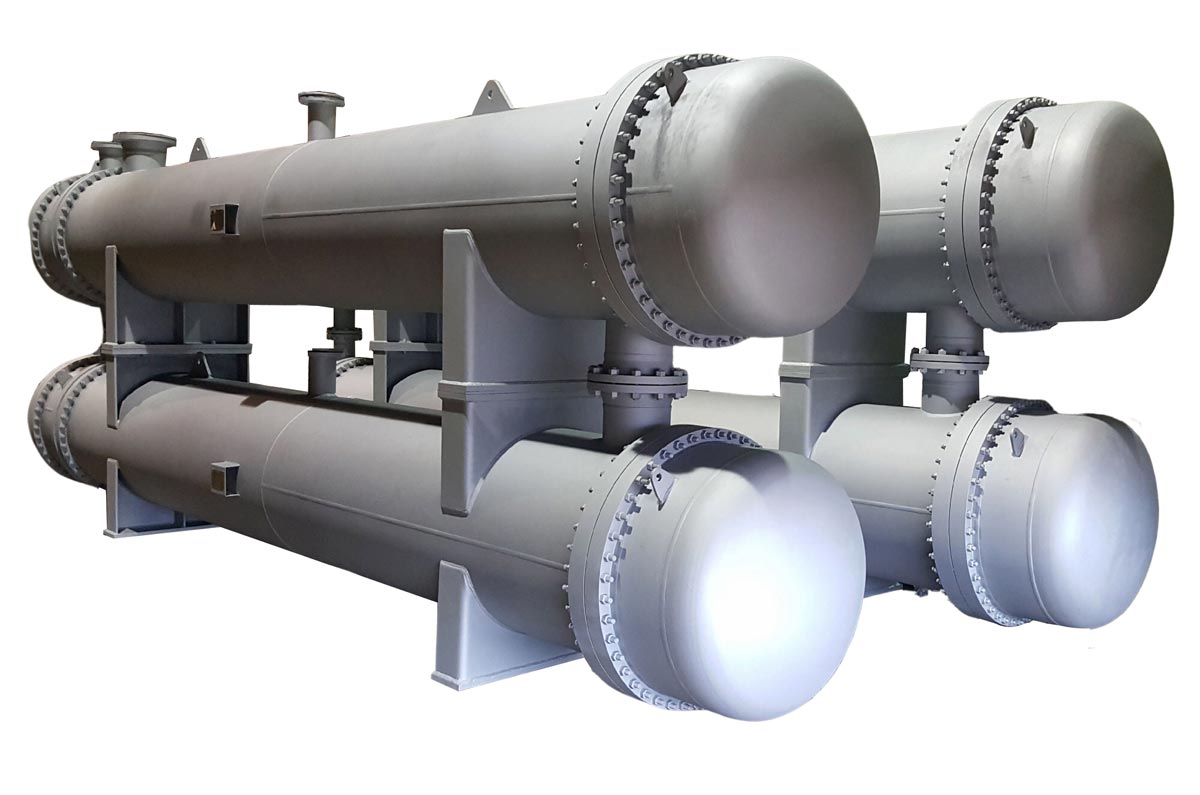
A: The primary types of heat exchangers used in industry include shell-and-tube, plate, air-cooled, and spiral heat exchangers. Shell-and-tube exchangers consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid, typically used for high-pressure applications and large heat duties. Plate heat exchangers use corrugated plates to transfer heat efficiently and are compact, making them suitable for lower pressure and smaller scale applications. Air-cooled heat exchangers use ambient air to cool fluids, often applied where water is scarce. Spiral heat exchangers have two spiral channels and are good for viscous fluids and fouling services. Each type has advantages depending on factors like pressure, temperature, fluid properties, and maintenance needs. For more detailed information, refer to the 'Heat Exchanger Design Handbook' or resources like the [Chemical Engineering's Heat Exchanger Basics](https://www.cheresources.com/content/articles/heat-exchanger-basics).