Preview this course
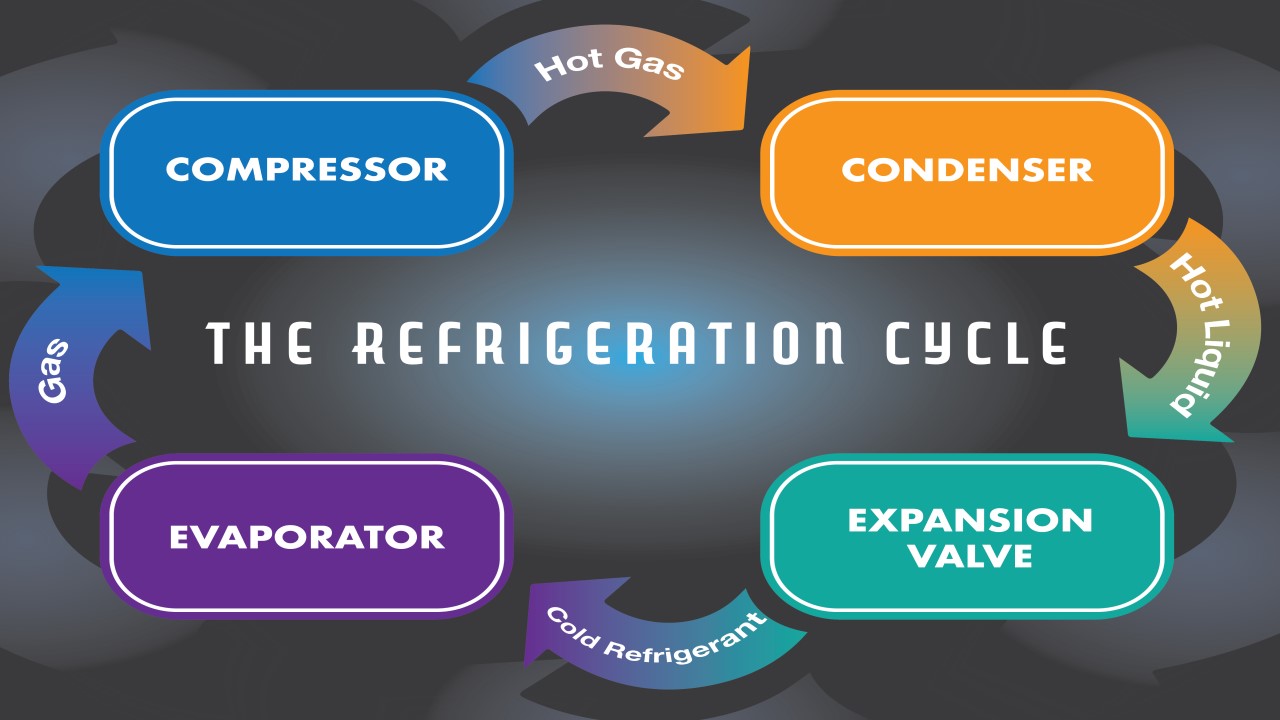
Piping Material Engineering
$ 170
3 already enrolled!
Course content
The course is readily available, allowing learners to start and complete it at their own pace.
Why people choose EveryEng
Industry-aligned courses, expert training, hands-on learning, recognized certifications, and job opportunities—all in a flexible and supportive environment.
- Industry Veteran
- Trainer Review
❮
❯